Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas due to the passage of an electric current.
This technique can be used to make hydrogen gas, the main component of hydrogen fuel, and breathable oxygen gas, or can mix the two into oxyhydrogen, which is also usable as fuel, though more volatile and dangerous.
It is also called water splitting. It ideally requires a potential difference of 1.23 volts to split water
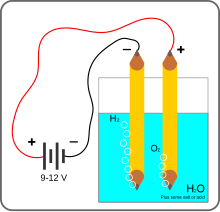
At home experiment:
What You Need:
- 6-volt or 9-volt battery
- Two alligator clip leads or insulated wire
- Beaker or glass
- Piece of thin cardboard or card stock
- Two #2 pencils
- Table Salt (NaCl) or Sodium hydroxide(NaOH; it can be dangerous)
N.B: A salt is used to increase ions in water and improve its conductivity. Acid can be lethal
- 6-volt or 9-volt battery
- Two alligator clip leads or insulated wire
- Beaker or glass
- Piece of thin cardboard or card stock
- Two #2 pencils
- Table Salt (NaCl) or Sodium hydroxide(NaOH; it can be dangerous)
What You Do:
- Fill the beaker or glass with warm water mixed with the salt.
- Carefully remove the erasers and metal sleeves so you can sharpen both ends of each pencil. These pencils are your electrodes. The graphite in them will conduct electricity, but won’t dissolve into the water.
- Cut a piece of the cardboard to fit over the beaker, then punch two holes in the center of the cardboard about an inch apart. Push the pencils through the holes and set them in the glass or rubber. They should extend into the water, but not touch the bottom of the glass. The cardboard will hold them in place.
- Connect each pencil to the battery with an alligator clip lead attached to the exposed graphite (pencil lead). If you don’t have alligator clip leads, use two lengths of wire and strip an inch of insulation off each end. Wrap the wire around the graphite of each pencil and connect the wires to the battery. You may need to use tape to hold the wires in place.
- Fill the beaker or glass with warm water mixed with the salt.
- Carefully remove the erasers and metal sleeves so you can sharpen both ends of each pencil. These pencils are your electrodes. The graphite in them will conduct electricity, but won’t dissolve into the water.
- Cut a piece of the cardboard to fit over the beaker, then punch two holes in the center of the cardboard about an inch apart. Push the pencils through the holes and set them in the glass or rubber. They should extend into the water, but not touch the bottom of the glass. The cardboard will hold them in place.
- Connect each pencil to the battery with an alligator clip lead attached to the exposed graphite (pencil lead). If you don’t have alligator clip leads, use two lengths of wire and strip an inch of insulation off each end. Wrap the wire around the graphite of each pencil and connect the wires to the battery. You may need to use tape to hold the wires in place.
What Happened:
As soon as you connect the wires to the battery, you will see bubbles appearing around each of the pencil tips in the water and floating upward. Those bubbles are the components of water—hydrogen and oxygen gas—that have been split apart by the electricity as it travels through the water from one pencil to the other. The pencil attached to the negative terminal of the battery collects hydrogen gas while the one connected to the positive terminal collects oxygen. Does one pencil collect more bubbles than the other? Which one? Why do you think this is?
(Hint: Water’s chemical name is H2O because it has two hydrogen atoms to every one oxygen atom.)

Wow. This is wonderful. I can't believe this is happening. Well done 👍🏽👍🏽👍🏽👍🏽👍🏽
ReplyDeleteThank you😁
DeleteOkkk
ReplyDelete😊
Delete